Table of Contents
- Evolution of Hydraulic Lifting Systems
- Key Components and Mechanisms
- Applications in Modern Infrastructure
- Technological Advancements
- Safety and Efficiency Benefits
- Future Trends
- Final Thoughts
Modern infrastructure is evolving rapidly, and so are the technologies that support it. A central player in this transformation is hydraulic lifting systems. Advancements in hydraulic engineering now enable us to handle heavier loads, enhance safety, and execute large-scale projects with unprecedented efficiency. One striking example of this technological leap is the hydraulically raised substructure for land drilling rigs, which enables oil and gas projects to move and adjust sizable platforms with minimal manpower and greater stability.
Whether in construction, transportation, or energy sectors, hydraulic lifting solutions are integral to tackling the most demanding operations and ensuring rapid, safe project delivery. Thanks to intelligent controls, innovative designs, and robust components, industries can accurately and securely lift, relocate, or install massive structures, meeting stringent timelines and safety standards.
The adoption of hydraulic lifting isn’t just for mega-projects. Even smaller undertakings across urban and industrial landscapes are benefiting from the flexibility and reliability of these systems, making them a cornerstone for both routine maintenance and cutting-edge development work. From bridge construction to wind turbine assembly, these systems offer scalable solutions to nearly any lifting challenge.
Evolution of Hydraulic Lifting Systems
Hydraulic lifting systems have evolved significantly since their initial introduction in industrial settings. The earliest models operated on the principles of fundamental fluid mechanics, utilizing simple pumps, valves, and pistons for basic load handling. Over time, rising infrastructural demands spurred innovation. Advanced compositions and rigorous engineering standards have given rise to high-capacity equipment, such as hydraulic gantries, which enable the precise and safe movement of equipment weighing hundreds of tons. The move from manual operation to electronically and digitally managed systems represents a leap in both productivity and usability. Major projects, such as those involving bridge construction and modular building assembly, now routinely leverage these systems for their reliability and accuracy.
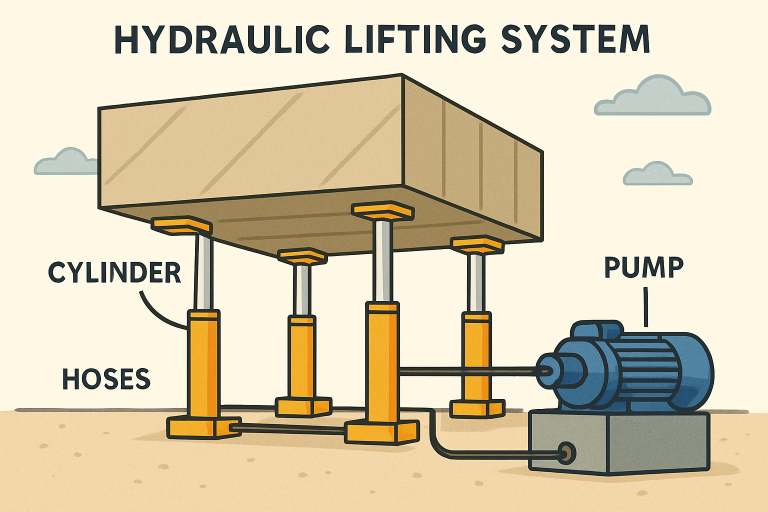
Key Components and Mechanisms
At the core of every hydraulic lifting system are several essential elements that ensure successful operation:
- Hydraulic Cylinders: Convert hydraulic fluid pressure into strong, linear lifting forces, making them the primary movers in any hydraulic system.
- Pumps: Generate continuous fluid flow to power the cylinders, with options for both manual and automated operation.
- Valves: Precisely manage the direction and volume of hydraulic fluid, granting careful control over lift speed and load balance.
- Reservoirs: Store hydraulic fluids and help dissipate heat generated during heavy-duty operations.
- Control Systems: Range from basic levers to advanced computerized interfaces, enabling synchronized and secure multi-point lifts.
Together, these components create a synergistic system capable of achieving feats that would be impossible with conventional mechanical lifting methods.
Applications in Modern Infrastructure
Hydraulic lifting systems are pivotal across numerous infrastructure projects, enabling the creation and maintenance of modern society’s backbone:
- Construction: Hydraulic lifters streamline building assembly, bridge erection, and heavy component positioning, reducing project durations and onsite risks.
- Energy Sector: Wind farm development and power plant maintenance rely on hydraulics for lifting turbines, generators, and large-scale equipment.
- Transportation: Essential for installing railway segments, elevating terminals, and ensuring safe and efficient port operations.
Technological Advancements
Innovation is reshaping hydraulic lifting solutions in several ways:
- Modular Designs: New systems are configurable to meet changing project needs, enabling modular expansion or contraction to accommodate varying load demands.
- Precision Control: Digital interfaces and real-time feedback systems enable millimeter-precise movements and synchronized lifts, minimizing errors and maximizing safety.
- Energy Efficiency: Machine learning tools are now being utilized to optimize energy usage, extend equipment lifespan, and reduce operational costs, thereby addressing both sustainability and economic objectives.
These technological strides are not only meeting but exceeding safety regulations and client expectations, making previously impossible tasks executable and routine.
Safety and Efficiency Benefits
Hydraulic lifting systems are designed with safety and efficiency as top priorities:
- Enhanced Safety: Controlled hydraulic operations drastically reduce manual labor risks and prevent common workplace accidents. Hydraulic platform lifts, for example, have been shown to reduce fall-related incidents by up to 73% compared to scaffolding.
- Increased Efficiency: These systems enable faster setup, repositioning, and execution, supporting the timely and budget-friendly delivery of projects.
- Versatility: Adaptable for use in tight urban sites or sprawling industrial complexes, hydraulic systems cater to a broad spectrum of project scales and requirements.
Their role in accelerating timelines and improving site safety highlights why hydraulic lifters are preferred solutions in industries worldwide.
Future Trends
Looking ahead, hydraulic lifting technology is poised to adopt more smart features and sustainable practices:
- Automation: Research and development are steering towards self-operating, AI-driven hydraulic lifts that require minimal human intervention, further improving consistency and safety.
- Sustainability: Next-generation systems are experimenting with hydrogen fuel cells and electric power to reduce environmental impact and meet tightening emissions standards.
- Digital Integration: IoT sensors and predictive analytics are expected to become standard, enabling remote monitoring, predictive maintenance, and optimized asset management to maximize uptime and longevity.
These trends will define the future of infrastructure, ensuring more resilient, intelligent, and sustainable lifting operations.
Final Thoughts
Hydraulic lifting systems are indispensable for the successful execution of modern infrastructure projects, from high-rise construction to renewable energy installation. With continuous advancements in safety, capacity, and technology, these systems are transforming the construction and maintenance landscape, delivering remarkable improvements in project delivery, worker safety, and operational efficiency. As infrastructure needs continue to evolve, the adoption and innovation of hydraulic lifting will only become more critical in shaping a sustainable and technologically advanced future.